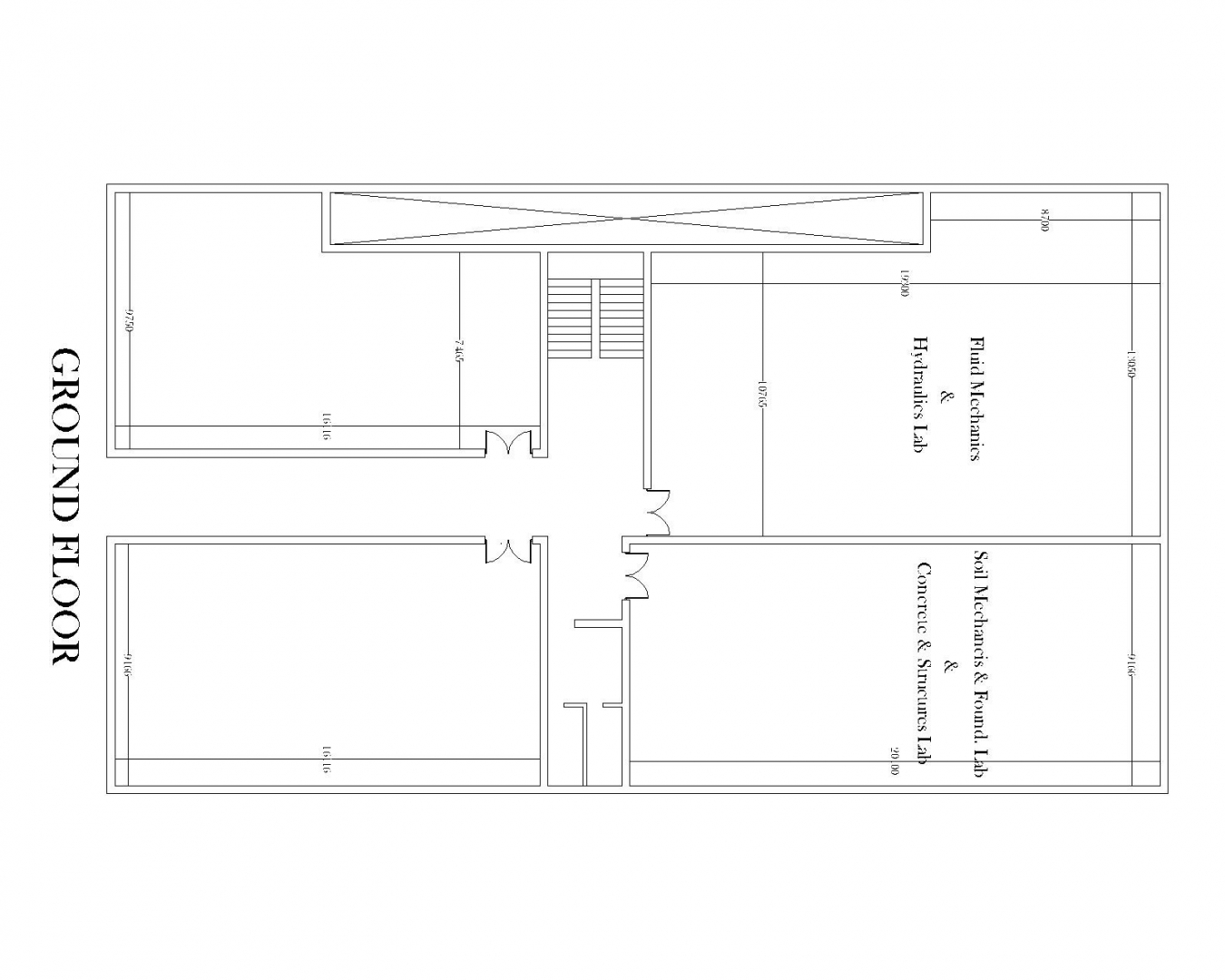
The laboratories used by the Civil Engineering Department are located in a separate building called workshop area. The laboratories have adequate instruments for carrying out experimental work for courses, final year projects, research projects and consultancy, community services. The laboratories are maintained and upgraded time to time. The laboratories are capable of delivering the course curriculum. The laboratories serving the teaching and research activities within the department are as follows:
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Laboratory
- Surveying Laboratory
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Laboratory
- GIS Laboratory
- Concrete and Structural Laboratory
- Highway and Building Materials Laboratory
- Environmental Engineering Laboratory
Table 1 Summarizes the specific laboratory facilities, their purpose (i.e., which classes are supported), condition, adequacy and space. The layouts of the laboratories are shown in figure 1. The laboratories and the activity therein contribute towards achieving the following ABET outcomes:
Outcome b: An ability to design and conduct experiments, analyze and interpret data..
Outcome c: An ability to design a system, component or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, constructability, and sustainability
Outcome f: An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility
Outcome g1: An ability to communicate effectively (written)
Outcome i: A recognition of the need for and an ability to engage in lifelong learning
Outcome k: An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice
Table 1: Details of the laboratories
|
S. No |
Name of the Lab |
Location |
Area in Sq. m |
|
1. |
Environmental Engineering Lab |
W4/2/8 |
90 |
|
2. |
Soil Mechanics And Foundation Engg. Lab |
W4/1/3 |
184.23 |
|
2. |
Structural Analysis Lab |
A/1/28 |
45 |
|
3. |
Concrete and Structures Lab laboratory |
W4/1/3 |
184.23 |
|
4. |
Hydraulic Lab |
W4/1/4 |
227.76 |
|
5. |
Fluid Mechanics |
W4/1/4 |
227.76 |
|
6 |
Surveying Lab |
W4/2/4 |
70.72 |
|
7 |
Transportation Lab |
W4/2/2 |
102.59 |
|
8 |
GIS Lab |
A/1/38 |
54 |
|
9 |
Hydrology Lab |
W4/1/4 |
227.76 |
Figure 1: Layout of Civil Engineering Laboratory
A. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Laboratory
The Soil Mechanics Laboratory is utilized to determine the soil properties (physical, engineering, and strength parameters) and foundation design parameters. The following tests are conducted in this laboratory:
- Moisture content of soil
- Bulk and dry density of soil
- Specific gravity of soil
- Sieve analysis of soil sample
- Hydrometer analysis of fine soil
- Atterberg’s limit (liquid, plastic and shrinkage limits)
- Constant head permeability test of soil
- Falling head permeability test of soil
- Standard proctor test of soil
- Direct shear test of soil
- Degree of compaction of soil
- Dynamic cone penetration test of soil
- Pocket penetrometer test of soil
- Untrained triaxial test of soil
- Unconfined compressive strength test of soil
- Consolidation test (Odometer) of soil
- California bearing ratio test (CBR) of sub-grade soil
B. Structural Analysis Laboratory
The Structural Analysis Laboratory is utilized to determine the structural parameters of RCC and Steel structure components. The purpose of the lab is to let the student utilize the available software for structural analysis. There is no specific time duration but the students can arrange
C. Surveying Laboratory
The Surveying Laboratory is utilized to determine the topographical features of the land surface. The following tests are conducted in this laboratory:
- To erect perpendicular by 3-4-5 rule using Tape
- Determination of elevation of various points with auto level by collimation method or Height of Instrument method.
- Determination of elevation of various points with auto level by Rise and Fall Method
- Fixing bench mark with respect to temporary bench mark with precise level by fly leveling using height of instrument method
- Fixing bench mark with respect to temporary bench mark with precise level by fly leveling using Rise and Fall Method
- Determination of the Multiplying and additive constant of given Tachometer
- Determination of elevation of points and horizontal distance between them by Tachometric survey.
- Measurement of horizontal and vertical angle using Total Station
- Demonstration of stereoscopes for stereoscopic viewing of Photographs
- To determine area of regular and irregular area using Digital Planimeter
- To locate various points using GPS Survey
- Setting out Simple circular curve using Rankine Method
D. Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics and Hydrology Laboratory
The Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics and Hydrology Laboratory is utilized to determine the fluid properties and hydraulics parameters of fluid and hydrology system.
|
S. No. |
Experiment |
|
1. |
|
|
2. |
Seepage through an Earth Dam |
|
3. |
Draining Effect of a Tile line |
|
4. |
Draining Effect of an open trench |
|
5. |
Uplift pressure on foundation structures |
|
6. |
Changing Uplift Pressure by changing length of flow lines |
|
7. |
Reduction of uplift pressure by draining |
|
8. |
Reduction of lateral thrust on a retaining wall by draining |
|
9. |
Quicksand |
|
10. |
Stability of an Earth Dam |
|
11. |
Well-draining |
|
12. |
The Hydrological Cycle and Rainfall-Runoff relationship |
|
13. |
Stream flow from a single storm |
|
14. |
Stream flow from multiple storm |
|
15. |
Stream flow from an impermeable catchment |
|
16. |
Effect of land drainage on run-off hydrograph |
|
17. |
Effect of direction of storm movement |
Hydraulics Lab Experiment List
|
S. No. |
Experiment |
|
1 |
Characteristics of Flow over a sharp Crested Overshot Weir |
|
2 |
Characteristics of Flow over a Broad Crested Weir |
|
3 |
Characteristics of Flow over a Crump Weir |
|
4 |
Discharge beneath a sluice gate |
|
5 |
Force on a sluice gate |
|
6 |
Force on a sluice gate |
|
7 |
Derivation of specific energy Equation |
|
8 |
The Hydraulic Jump |
|
9 |
Characteristics of Flow through a Venturi Flume |
|
10 |
Characteristics of Flow through a culvert |
|
11 |
Characteristics of Flow Around Flow Splitters |
|
12 |
Characteristics of Flow over a Dam spillway |
|
13 |
Characteristics of Flow through a siphon spillway |
|
14 |
Characteristics of Flow through an air regulated siphon |
|
15 |
Characteristics of Flow under a radial gate |
|
16 |
Characteristics of Flow over false floor sections |
|
17 |
Characteristics of Flow over a gravel bed |
E. GIS Laboratory
The GIS Laboratory is utilized to determine and represent the spatial parameters. The following practical and tutorials are conducted in GIS laboratory:
|
CODE |
DESCRIPTION |
|
EX GIS 1 |
Arc GIS 9 Software Overview |
|
EX GIS 2 |
Working with ArcMap |
|
EX GIS 3 |
Working with ArcTool Box |
|
EX GIS 4 |
Georeferencing and Projection |
|
EX GIS 5 |
Spatial Data Entry-Digitization |
|
EX GIS 6 |
Spatial Data Editing |
|
EX GIS 7 |
Non Spatial Data Entry |
|
EX GIS 8 |
Query & Analysis |
|
EX GIS 9 |
Map Composition |
|
EX GIS 10 |
Generation of DEM |
|
EX GIS 11 |
Familiarization with different Types of GPS receivers |
|
EX GIS 12 |
Checking of existing map coordinates using single GPS |
|
EX GIS 13 |
Calculation of Coordinates with differential GPS receiver |
|
EX GIS 14 |
Survey of Small area with the help of GPS receivers |
F. Concrete and Structural Laboratory
The Concrete and Structural Laboratory is utilized to determine the strength parameters of RCC blocks used in various types of civil structures. The following tests are conducted in this laboratory:
- Normal Consistency of Cement
- Initial and Final Setting Times of Cement
- Fineness of Cement
- Specific Gravity of Cement
- Compressive Strength of Cement Mortar (Machine Need Calibration and Checking)
- Flexural Strength of Cement Mortar (Machine Need Calibration and Checking and Checking)
- Tensile Strength of Cement Mortar (Machine Need Calibration and Checking)
- Soundness of Cement
- Fineness Modulus of Fine and Coarse Aggregate
- Bulking of Fine Aggregate
- Specific Gravity and Bulk Density of Coarse and Fine Aggregate
- Slump Tests of Fresh Concrete
- Compressive Strength of Concrete (Machine Need Calibration and Checking)
- Flexural Strength of hardened Concrete (Machine Need Calibration and Checking)
- Non-destructive Testing of hardened concrete using Schmidt hammer
- Non-destructive Testing of hardened concrete using Portable Ultrasonic Pulses Velocity Test (PUNDIT)
G. Highway and Building Material Laboratory
The Highway and Building Material Laboratory is utilized to determine the strength parameters of bitumen and other building materials used in construction. The following tests are conducted in this laboratory:
H. Environmental engineering laboratory
The Environmental Engineering Laboratory is utilized to analyze the parameters of water and waste water. The following tests are conducted in this laboratory:
- Determination of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in Water sample.
- Determination of Total Suspended Solids (TSS).
- Determination of Settle-able Solids (SS).
- Determination of Volatile Suspended Solids (TDS).
- Measuring pH of Water/Waste water.
- Measuring Electrical Conductance.
- Measuring Turbidity of Water/Waste water.
- Measuring total alkalinity of a given water sample and type of alkalinity.
- Measuring total hardness of a given water sample.
- Determining the type of hardness.
- Measuring the Dissolved Oxygen in a given water/Waste water sample.
- Measuring Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) of a given effluent sample.
- Measuring Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) of a given effluent sample.
- Measuring Total coli form bacteria in a given sample.